What is inflammation?
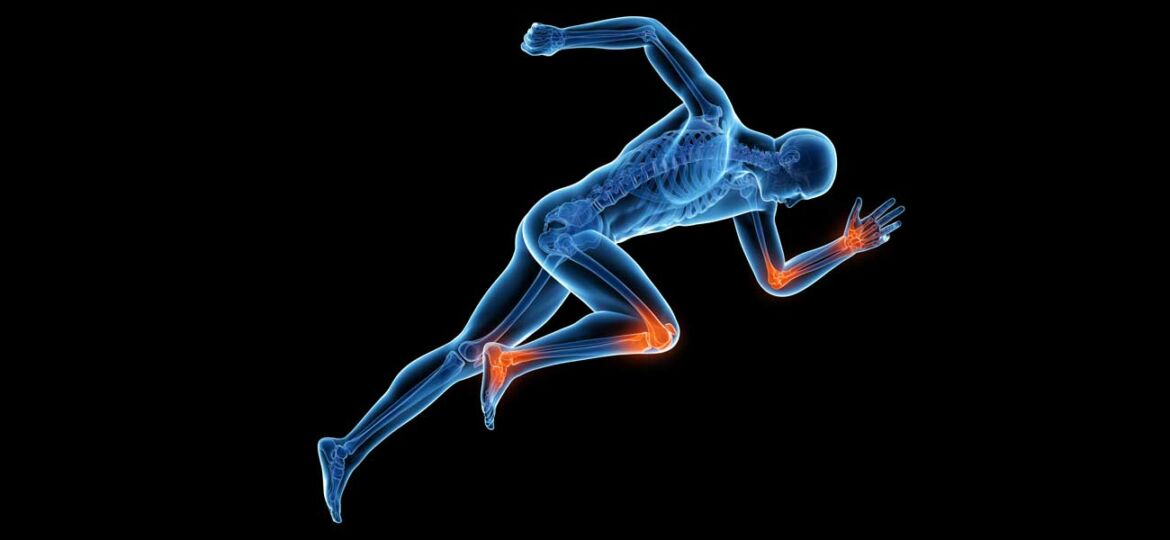
Swelling, redness, itchiness or burning of the skin after an injury or a few days long (“acute”) experience such as something caused by food or alcohol, or on a more long-term (“chronic) basis, deep, sharp and resiliently present pains, cramps and aches such as backache, a throbbing knee or recurring migraines are all ways that inflammation shows up in our life.
When the body faces what it perceives as a threat or possible invader (from a splinter or any foreign object to a pathogen such as bacteria and viruses), its immune response kicks in. In its bid to protect the organism from harm, it releases proteins and antibodies and blood flow to the threatened area. Infections, toxins and injuries are confronted by the body in this way, leading to what we call inflammation.
How does inflammation affect the body and mind?
Everyone experiences various forms of acute inflammation throughout their life, as it is a natural and inevitable part of recovery, but when inflammation becomes chronic, it can wreak havoc in our life. If left unattended, long-term, slow inflammation will not magically go away. Studies have shown that it can lead to the damage of healthy organs, cells and tissues, causing tissue death, internal scarring and even damaging the DNA in healthy cells, eventually leading to illnesses like cancer and diabetes.
The effects of chronic inflammation on the brain are also particularly harmful to life-threatening; as high levels of inflammatory markers can disrupt the blood-brain barrier, neurotoxins can flood the brain and cause the creation of anomalous tissue structure, leading to brain inflammation. Common causes of inflammation include:
- High levels of stress
- Poor diet and imbalanced gut microbiome
- Autoimmune diseases, arthritis, rheumatism or gout
- Allergic reactions to environmental factos
As a result, this inflammation can cause an entire host of symptoms in both body and brain, like frequent infections, gastrointestinal disturbances, depression or anxiety, pains, chronic fatigue, sudden weight gain or loss, insomnia, cognitive and/or memory decline (often resulting in dementia or Alzheimer’s), depression, mood disturbances and anxiety.
What daily habits prevent or reverse inflammation?
Although it’s always a good idea to immediately see your doctor if you are experiencing long-term inflammation that affects you heavily, there are several things you can do to battle milder or consistent forms of inflammation. Research has shown that the following steps are key:
- Cut out or significantly regulate obvious toxins like cigarettes, alcohol and sugar. Taking any or all of these three steps has been shown to dramatically reduce inflammation-related problems within weeks.
- Introduce regular exercise into your life. Both aerobic exercise and yoga are thought to offer substantial benefits to the inflamed mind and body. Also, managing your weight (especially focusing on reducing abdominal fat) through exercise cam be a positive anti-inflammatory solution.
- Sleep tight! During sleep our body detoxifies the brain and body, bringing a new balance. Irregular or disturbed sleep can prevent this process from occurring, leading to the development or exacerbation of inflammation. Sleeping well enhances any anti-inflammatory mission.
Beating inflammation with the right diet
Throughout the ages, the diet we follow has consistently been linked to our overall mental, physical and even emotional wellbeing, and in a multitude of cases food has proven to indeed be, as Hippocrates said, medicine. A natural, chiefly organic, balanced and wholesome duet including a lot of fresh vegetables, herbs and fruits, whole grains, pulses and quality cuts of fish and meat can be a game changer when it comes to inflammation.
The top anti-inflammatory foods include tomatoes, extra virgin olive oil, nuts and seeds, leafy greens, fruits like sour cherries, blueberries and strawberries, and fatty fish. Introducing herbs and spices into your daily diet is also highly beneficial; turmeric (always used along with a little black pepper in order for it to be effective) is especially lauded as a top anti-inflammatory agent, while cinnamon, ginger, garlic, cumin and cayenne pepper are also shown to offer benefits.
Although no conclusive research has been made, intermittent fasting or periods of following a mainly vegan/plant-based fast (up to around 40 days) is a method practiced by humanity for millennia as an effective detox from inflammation-causing toxins.
As Always, drinking plenty of (ideally filtered) water and cutting down on irritants like alcohol and coffee are also conducive to fighting inflammation.
Finally, make sure that when you do consume foods that come out of packets, cans or jars, you read the ingredients carefully. Anything including added salt, sugar or glucose, preservatives and other chemicals is best avoided.
Are your body or mind affected by inflammation, or close to being hit by inflammation-related disease or symptoms? The best and easiest way to find out is by using the Biostarks home blood test kit and finding out. Click here to order yours now and look forward to receiving thorough information and customized expert advice on your personal condition.